Obesity is a prevalent, complex progressive and relapsing chronic disease, characterized by abnormal or excessive body fat (adiposity), that impairs health.
Causes of obesity

Genetics
Genetic and epigenetic variations contribute to obesity by influencing the function of metabolic pathways in the body and regulating neural pathways and appetite centers

Nutrition
Reducing the number of calories consumed by 500 to 1,000 calories a day may be expected to result in a weight loss of 1 to 2 pounds per week, which is a healthy rate of weight loss. This should be approved by your physician
Hormones
Certain hormonal disorders such as Cushing’s Syndrome, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and certain eating disorders are linked to developing obesity

Medications
Many drugs used to treat common disorders promote weight gain such as antidepressants, corticosteroids, antihypertensives - among others

Environment
Access to affordable healthy food varies by ethnic, racial and socioeconomic factors
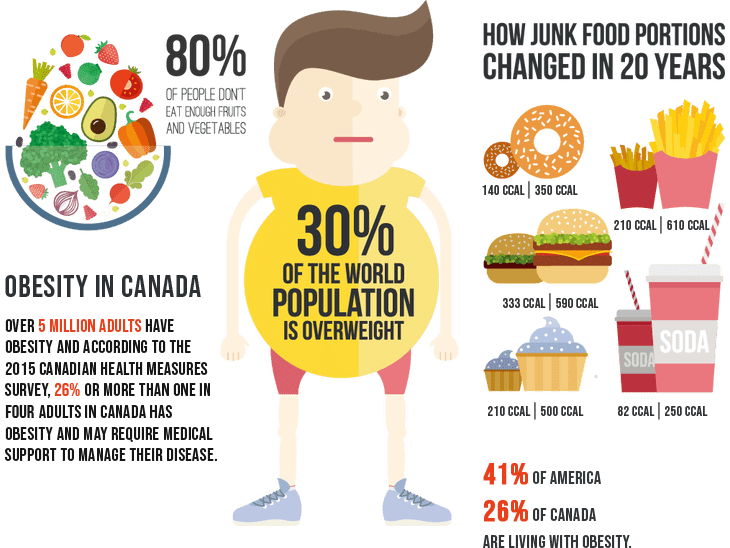
Current studies show that obesity decreases the lifespan by up to 8 years and is associated with
at least
236 other medical problems including
13 types of cancer, type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea,
high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and depression.
The three pillars of Obesity Medicine management that support nutrition and activity

Psychological Intervention

Pharmacotherapy